数据结构与算法 #
- Introduction 绪论
- Algorithm Analysis算法分析方法
- list, stack and queue线性表,栈和队
- Tree and Binary Trees树和二叉树
- Internal Sorting内部排序
- File processing and external sorting文件管理&外部排序
- Searching 查找
- Indexing索引
- Graph图
CHAPTER 1 #
Programs = Algorithm + Data Structures
程序设计:为计算机处理问题 编制一组指令集 算法:处理问题的策略 数据结构:问题中所涉及数据(集)的组织方式
Part 1 #
What is a data type(数据类型)? #
Class of data objects(某一类数据对象) that have the same properties(属性)
-
c语言中的基本数据类型:int, char, floadouble
-
构造数据类型:数组,结构体,共用体,枚举类型等
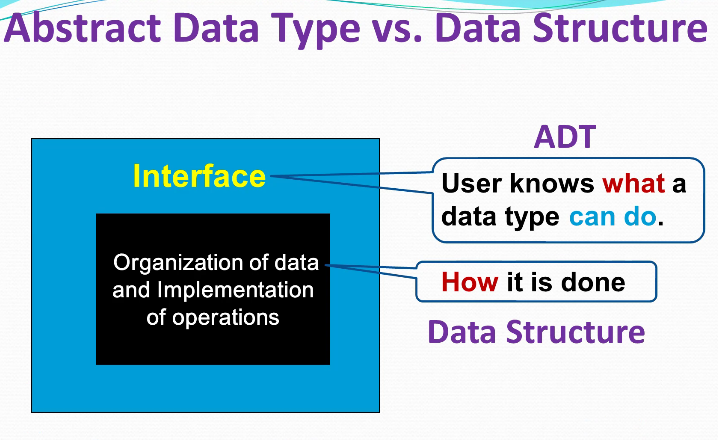
Abstract Data Type #
ADT= Data + Relation + Operations ADT(抽象数据类型)可用 (D, R,O)三元组表示其中:D是数据对象(数据集) R是D上的关系集(逻辑结构)O是对D的基本操作集
Data Structure #
e.g. 数据表是线性表这一抽象数据类型的具体实现,一种数据结构。
Data structure usually refers to an organization for Data in main memory (存储结构)and Operations implementation. A data structure is a physical implementation of an ADT.
- Each Operation associated with the ADT is implemented by one or more subroutines.
- an ADT may have multi data structure
-
Each data structure for a particular ADT has costs(代价) and benefits(优势).
-
A data structure requires: space to store data (空间需求); time to perform basic operation(时间需求), programming effort(编程容易度).
-
Rarely is one data structure better than another in all situations.
Logical vs. Physical Form #
Data items have both a logical and a physical form.
-
前者从逻辑关系上描述数据,与数据存储无关
- 例子,略
-
后者为计算机物理存储组织方式
- 顺序存储
- 连续存储单元
- 链式存储
- 指针链,不连续
- 顺序存储
1.2.3 Algorithm(算法)and Program(程序) #
Algorithm: a method or a process followed to solve a problem.
- A recipe (菜谱). An algorithm takes the input to a problem andtransforms it to the output.
- A mapping of input to output. A problem can have many algorithms.
Algorithm Properties
- It must be correct(正确) .
- It must be composed of a series of concrete steps(具体步骤).There can be no ambiguity as to which step will be performed next(确定性).
- It must be composed of a finite number of steps(有穷性· lt must terminate (可终止).
- It must have input and output(有输入输出).
Program
-
A computer program is an instance(实例), or concrete representation for an algorithm in some programming language.
-
Can run
1.3 Mathematical Background #
Set concepts(集合)
Logarithms(对数)
Summations(求和)
Recursion(递归)
Mathematical Proof Techniques(数学证明法)
CHAPTER 3 #
Topic
3.1 Introduction #
算法分析
two goals of computer program design.
- easy to understand, code, debug.
- The concern of Software Engineering
- efficient use of the computer’s resource
- The concern of data structures and algorithm analysis
Algorithm Efficiency #
How fast is an algorithm?
-
time How much memory does it cost?-
-
space How to Measure time/space Efficiency ?
Method1: Empirical analysis, simulation program, run and get a result Method2: Asymptotic analysis(渐进分析)
-
Step1: convert algorithm to time/space cost func.
-
Step2: analyze cost function using Asymptotic analysis 渐进分析
-
Algorithm Time cost function(时间代价函数) #
General format(通用形式):f(n) n is the size of a problem (the number that determines the size of input data)/问题规模
Best,Average, Worst Cases
Best case: fbest(n)given n, f(n) is smallest.
Worst case: fworst(n) given n, f(n) is largest.
Average case: fave(n) given n, f(n) in between. (前两者求平均)
好坏情况不同,根本原因是代码中有分支结构。
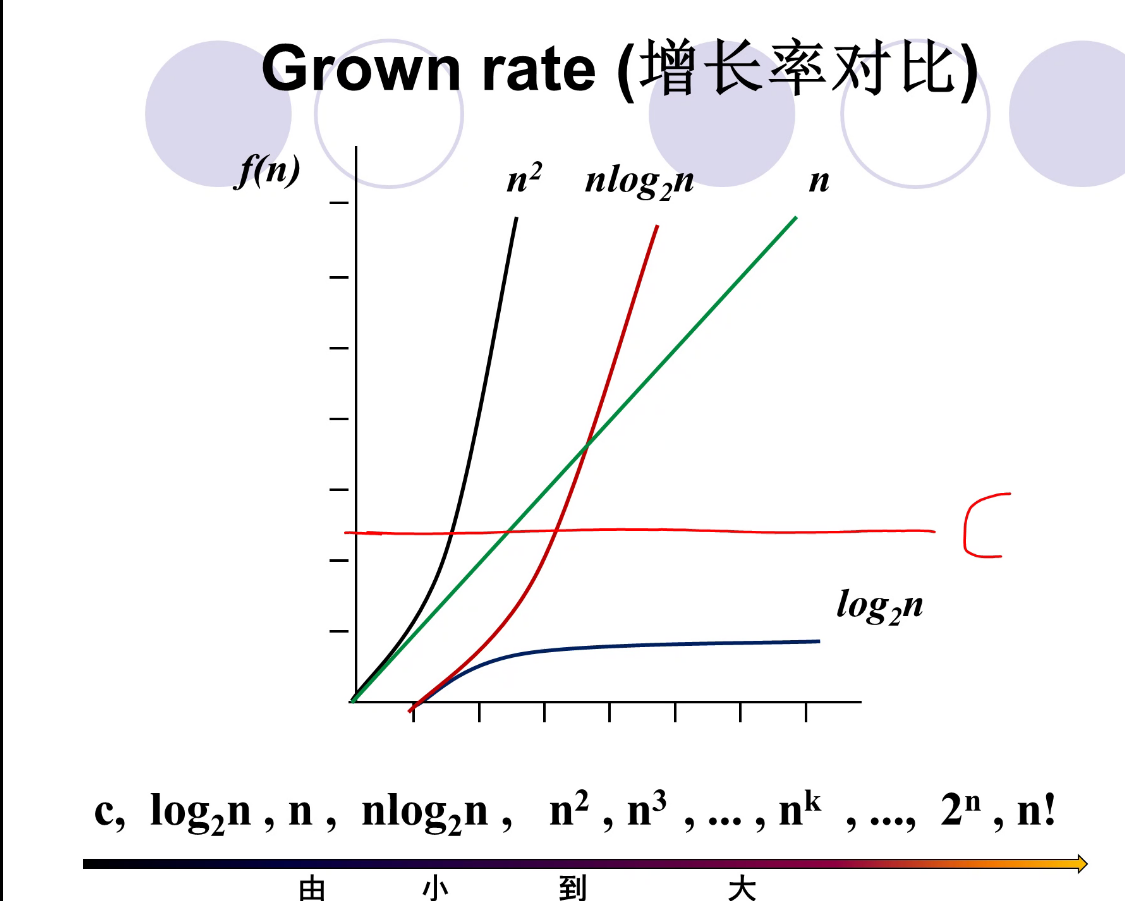
4.2 Growth rate(增长率) #
做算法性能分析时关心的不是fn)的具体形式,而是f(n)的growth rate(增长率) 即: n增长时,代价函数f(n)的增长速率 尤其关心当n很大很大时的f(n)的值 增长率越大,当n很大很大时的代价函数值越大
Linear Growth Rate(线性增长率) #
for(; i<n; i++)
Logarithmic Growth Rate(对数增长率) #
for(; i<n; i*=2)
Linear Logarithmic Growth Rate #
线性对数嵌套
Quadratic Growth Rate(平方增长率) #
线性线性嵌套
Dependent Quadratic Growth Rate(有依赖……) #
第二层嵌套关系j<i依赖于第一层i
仍然认为是平方增长率
3.3Algorithm Asymptotic Analysis(算法渐进分析) #
Algorithm efficiency(复杂度)is consideredwith only big sizes problem.即n很大情况
We are not concerned with an exact measurement ( f(n)) of an algorithm,我们关心的n很大时是f(n)的量级 估计代价函数f(n)的增长率作为算法的时间复杂度测度.
3.3.1(Big-O Notation) #
Definition(定义):
- For f(n) >=0,if there exist two positive constants c and n0 such that f(n)<=c g(n) for all n > n0, 系数为1的单项式 then we note f(n)= O(g(n)) or we say f(n) is in O(g(n))–f(n)的O描述为g(n).
Meaning(意义) :an upper bound/上限
- For all input data sets big enough (i.e., n>no),the algorithm always executes in less than cg(n) steps.
取值的不同意味着g(n)肯不同,我们取最紧凑的ver
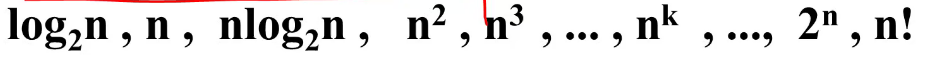
对于多项式,取最大项
3.3.2 Big-Q Notation #
-
Definition(定义): For f(n) >=0,if there exist two positive constants c and ng such that f(n)(>=g(n)for all n >n0 , then we note f(n)= (gn))
-
Meaning(意义):an lower bound/下限 For all data sets big enough (i.e., n > no), thealgorithm always executes in more than cg(n) steps.
3.3.3 Big- Notation #
Definition: If fn)- O(h(n)) and f(n)=2((we say fn)=(h(n)) Example:
f(n)=cn’+c,n. f(n)=O(n2 ) and fn)= Q(n2)
fn) = (n2)
3.3.4 Asymptotic Analysis Examples #
Simplifying Rules #
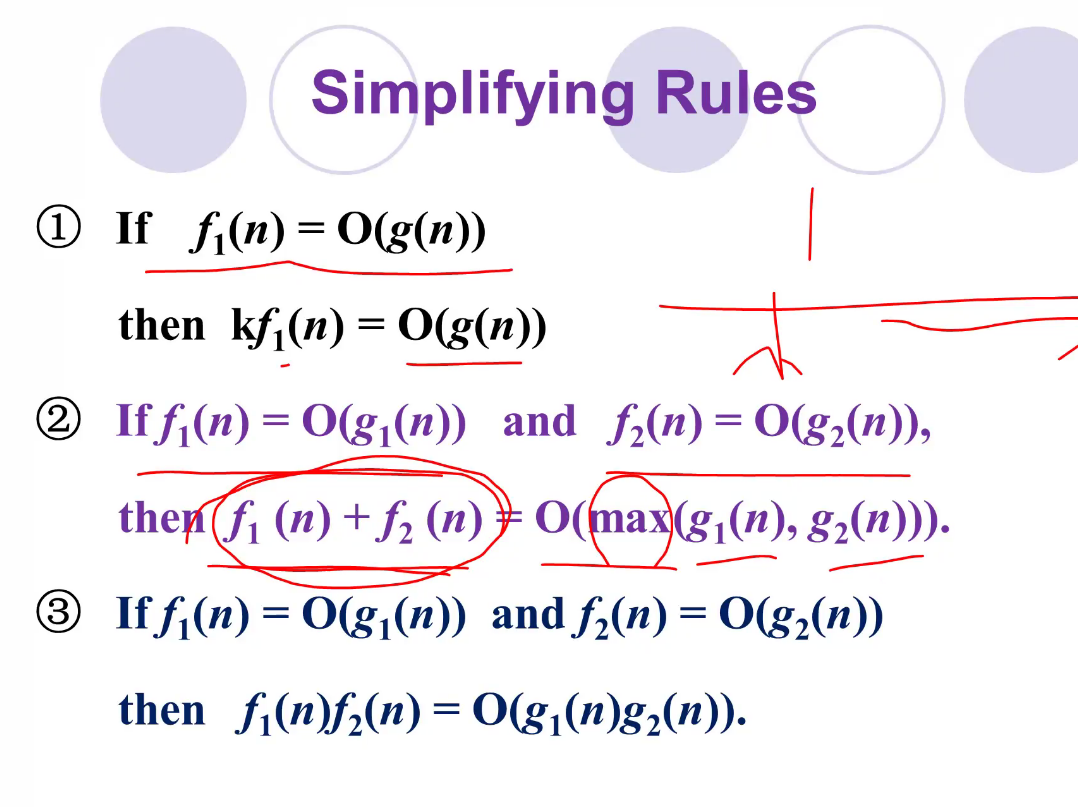
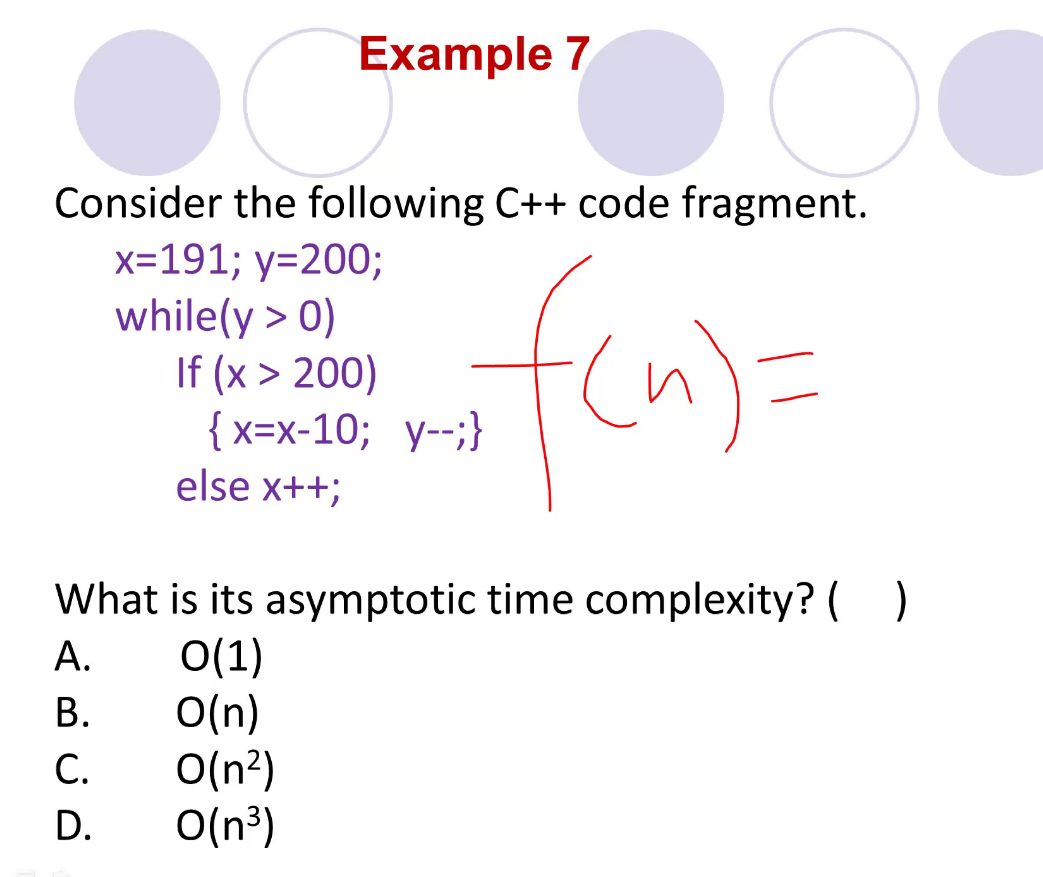
f(n) = C, 答案选A 这段代码跟我们的问题规模无关

3.3.5 Multiple Parameters #
3.4Space cost Analysis(空间代价分析)**** #
data structure S(n)
本章作业 3.3 3.9 3.12(b)(d)(g)(h)
